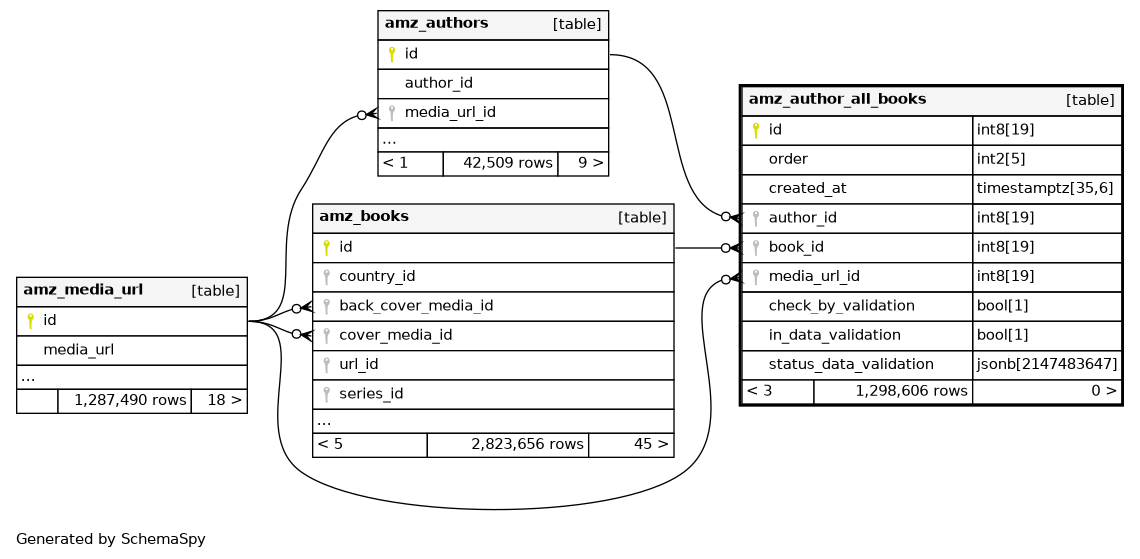
Columns
| Column | Type | Size | Nulls | Auto | Default | Children | Parents | Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | int8 | 19 | √ | null |
|
|
|||||
| order | int2 | 5 | √ | null |
|
|
|||||
| created_at | timestamptz | 35,6 | null |
|
|
||||||
| int8 | 19 | null |
|
|
|||||||
| book_id | int8 | 19 | √ | null |
|
|
|||||
| media_url_id | int8 | 19 | √ | null |
|
|
|||||
| check_by_validation | bool | 1 | null |
|
|
||||||
| in_data_validation | bool | 1 | null |
|
|
||||||
| status_data_validation | jsonb | 2147483647 | √ | null |
|
|
Indexes
| Constraint Name | Type | Sort | Column(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| amz_author_all_books_pkey | Primary key | Asc | id |
| amz_author_all_books_author_id_e71045a0 | Performance | Asc | author_id |
| amz_author_all_books_book_id_f1163b31 | Performance | Asc | book_id |
| amz_author_all_books_media_url_id_5e7ef84c | Performance | Asc | media_url_id |
| idx_author_all_books | Performance | Asc | author_id |
| idx_book_all_books | Performance | Asc | book_id |