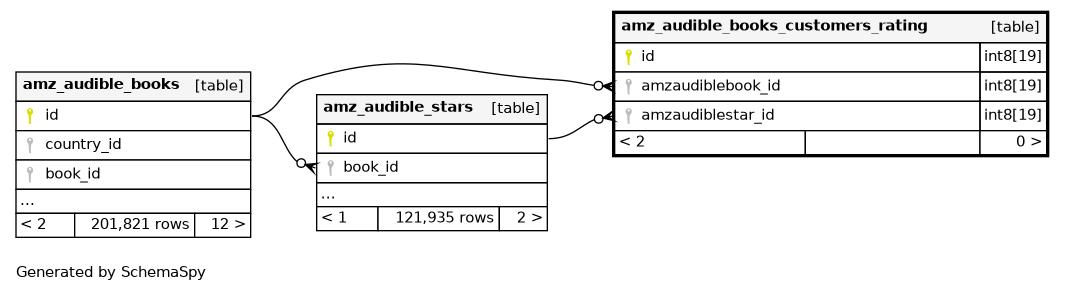
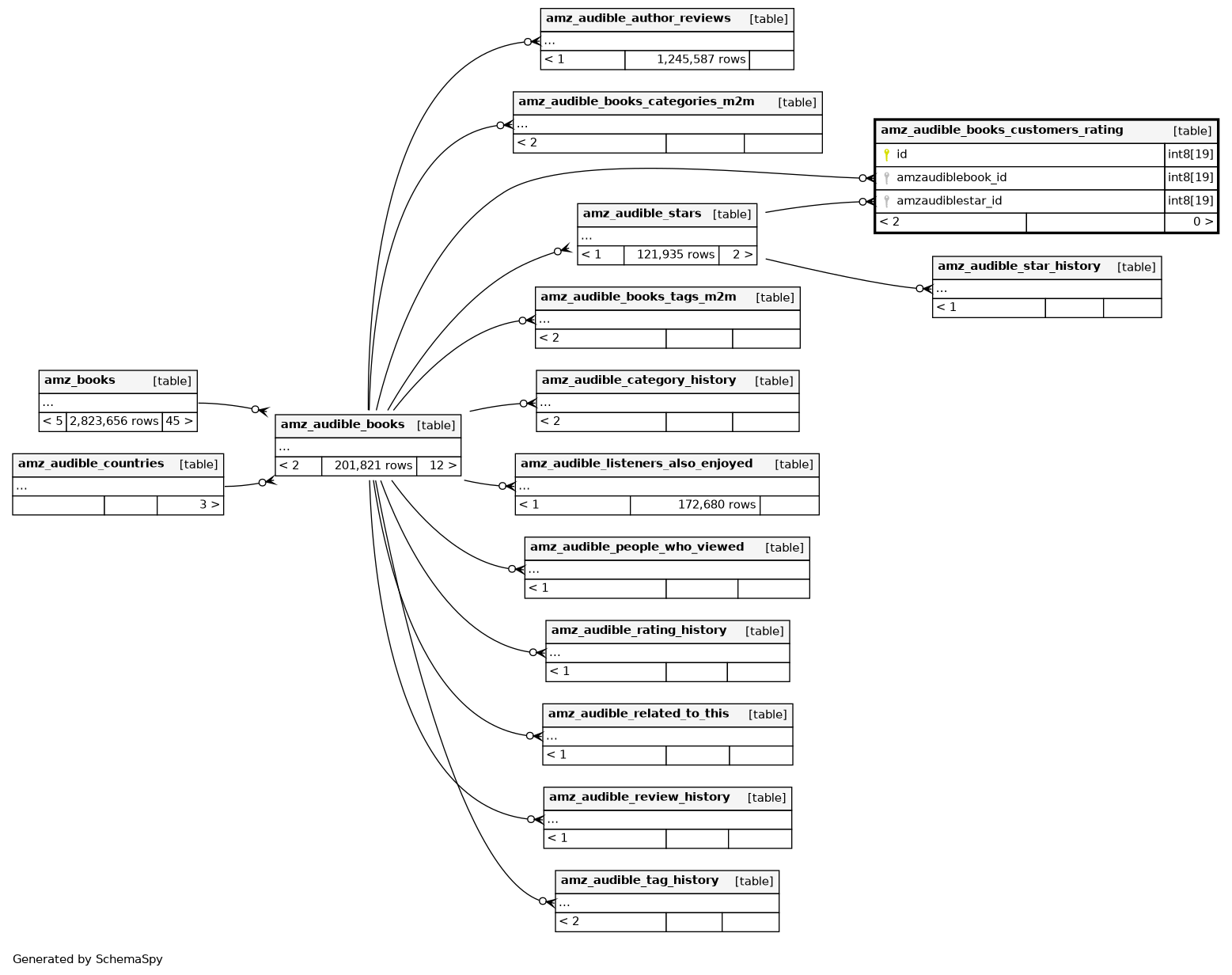
Columns
| Column | Type | Size | Nulls | Auto | Default | Children | Parents | Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | int8 | 19 | √ | null |
|
|
|||||
| amzaudiblebook_id | int8 | 19 | null |
|
|
||||||
| amzaudiblestar_id | int8 | 19 | null |
|
|
Indexes
| Constraint Name | Type | Sort | Column(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| amz_audible_books_customers_rating_pkey | Primary key | Asc | id |
| amz_audible_books_custom_amzaudiblebook_id_amzaud_18f6b5ec_uniq | Must be unique | Asc/Asc | amzaudiblebook_id + amzaudiblestar_id |
| amz_audible_books_customers_rating_amzaudiblebook_id_cbc7b259 | Performance | Asc | amzaudiblebook_id |
| amz_audible_books_customers_rating_amzaudiblestar_id_7f659ad7 | Performance | Asc | amzaudiblestar_id |